
Contact Dermatitis/ Allergic Contact Eczema
Contact Dermatitis develops from actual contact with an allergen. The allergen or allergy causing substance can be metal jewelry, a chemical or plant allergens (poison ivy, poison oak). Symptoms include redness, itching and burning in the area of the skin where contact was made.
If metal is irritating your skin, speak to your doctor about prescribing Psorizide®Forte, an all-natural oral medication that will desensitize you from a nickel/metal allergy in just a 16 week program – so that you will be able to wear costume jewelry/metal belt buckles again without fear of irritation.
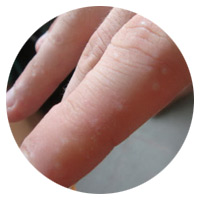
Dyshidrotic Dermatitis
This type of eczema only appears on the hands and feet. Symptoms include a blistering rash, burning and itching. It most often appears on the palms of the hands and less commonly on the soles of the feet.
Doctors typically prescribe Psorizide® Forte, which is a prescription only natural oral medication that like Loma Lux® Eczema works from the inside out to relieve symptoms.
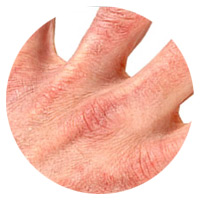
Seborrheic Eczema
Oily, waxy, scaly patches that appear on the scalp and sometimes on the face.
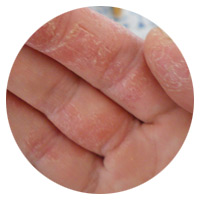
Hand Eczema
A red, blistery, burning rash that only appears on the hands.
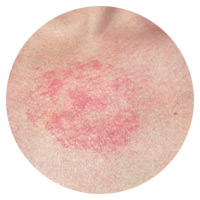
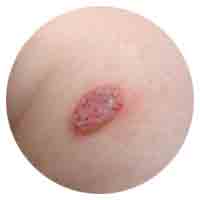
Nummular Eczema
Coin shaped, itchy marks that frequently occur after a skin injury or bug bite. It becomes instantly irritated when scratched.
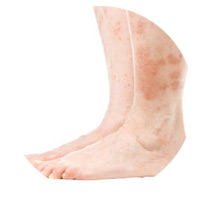
Stasis Dermatitis
This is a skin irritation caused by circulatory problems of pooling blood in the lower legs.
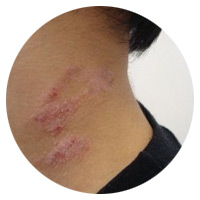
Neurodermatitis
Neurodermatitis occurs when the nerve endings in the skin become irritated (such as an insect bite). The nerve endings trigger severe itching, which worsens when scratched.
Atopic Dematitis
Atopic Dermatitis is the most common form of eczema and is increasing worldwide in prevalence. Atopic is derived from the Greek, meaning “strange”. Dermatitis is a term for inflammation of the skin.
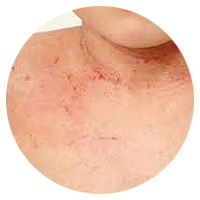
The skin becomes extremely itchy and inflamed – and sensitive to many irritants. Extremely dry skin forms dry, scaly patches that can also ooze or weep. Itching can be intense and lead to scratching, which makes symptoms worse, creating an itch-scratch cycle. Scratching can cause skin thickening and can lead to further complications, including bacterial infections. Itching makes everyday life intolerable. 1/3 of all eczema sufferers endure sleep disruption due to itching. Itching may be a sign of many other medical conditions that have nothing to do with eczema, so seeing a doctor will help in a proper eczema diagnosis. Typically, affected skin areas are the folds of the arms, back of the knee, wrist, face and hands.
Each person can experience their own unique combination of eczema symptoms, with the symptoms and severity of eczema varying over time.
About 65% of atopic dermatitis occurs before age 1 – with 90% occurring before age 5. A great majority of children, 65% continue to have eczema symptoms into adulthood.
There is some research that links atopic dermatitis with other atopic diseases (classic allergic diseases) such as seasonal allergies and allergic asthma. Some atopic dermatitis sufferers lack a protein called fillagrin that plays a vital role in the body’s ability to retain moisture. The skin becomes very dry, which reduces its ability to form a protective barrier.
Adults with atopic dermatitis are also predisposed to contact dermatitis – in occupations where there is a lot of frequent hand washing and/or exposure to chemicals involved. Also, some adults may be at risk of developing cataracts, so regular eye exams are recommended.
Moderate to severe eczema responds well to Eczemol®, a natural, oral prescription medication.
A June 2014 article within the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (JAAD) discussed research regarding pro & prebiotics for inflammatory skin conditions such as eczema. While their role in wound healing and photo protection (exposure to UV radiation) is promising, larger studies are needed before they can make a final recommendation as to probiotic use for eczema treatment.
